The need and demand for informal education is increasing, and it is becoming clear that it is often easier to learn the skills needed to be an effective developer and obtain a job in the industry through online courses and project-based work experience. The informal sector is particularly successful at preparing learners for jobs in tech, specifically for two main reasons: Firstly, the high demand that is not met by the formal education sector; and secondly, the nature of computing skills that tend to be well defined, specific, and measurable. For this reason, the popularity of disruptive coding educators is on the rise.
The growth of disruptive coding educators
The private sector is noticing the need to include the informal education sector and the “skills over degrees” motto is becoming increasingly popular. In IBM for example, nearly a third of new hires do not have formal four year college degrees. Marc van Zadelhoff, GM of IBM Security, highlighted that most of the skills needed in the sector do not require traditional four year college degrees, and that non traditional education platforms such as coding bootcamps are a great source for talent acquisition. Microsoft shared similar sentiments and has invested $25 million in Skillful to foster skills-orientated hiring, training, and education.
Online/ Informal coding educators to fill the digital tech skills gap
Online coding education is an increasingly important source of tech skills. The sector delivers a growing supply of programmers, from front-end to back-end developers. StackOverflow’s Developer Survey 2017 reports that 91.1% of developers are self-taught to some extent, and 44.1% of developers use online courses as a place to learn programming (Figure 1). Disruptive coding educators have a massive opportunity here to fill a large gap not being met by other formal education sources.
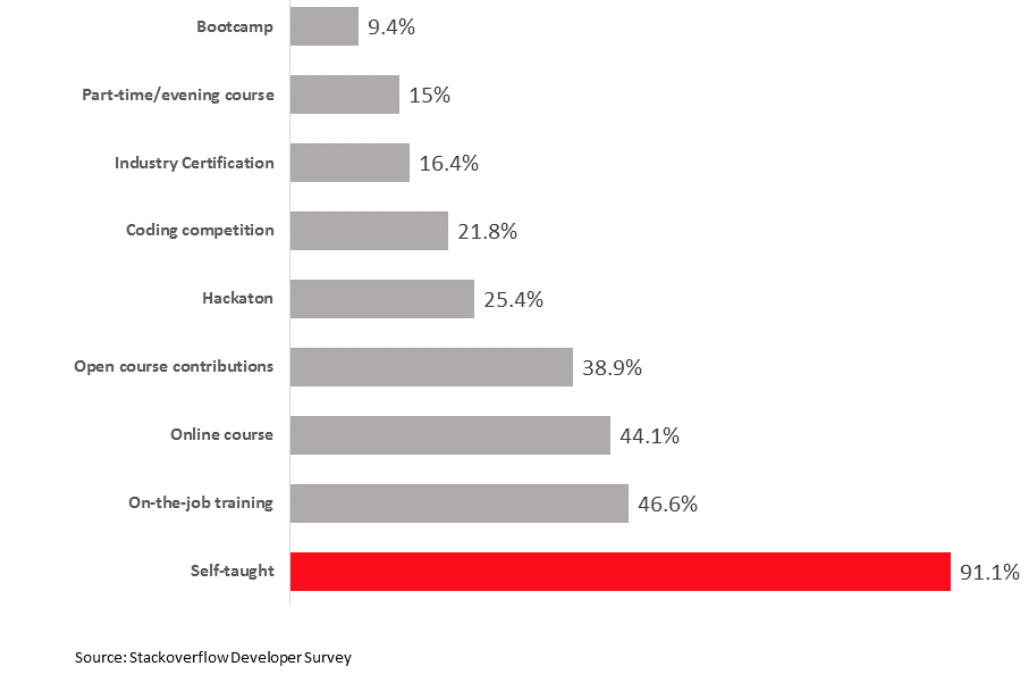
Figure 1: Developers’ types of education
Coding as a solution to unemployment
As the US struggles to provide jobs to the two-thirds of its adults who are 25 years or older and do not have a Bachelor’s degree, access to coding education can have a relieving effect on traditional hiring filters like formal education. As seen in Figure 2, already only 41% of software developers see formal education as important or very important, and only 26.9% of coders see formal education as somewhat important, as companies accept work experience as a substitute for a Bachelor’s degree.
From this, coding is seen as the new path to the middle class for people who lack four-year college degrees, as the skills-based jobs approach overrides the importance of educational pedigree and the limits of traditional class structures.
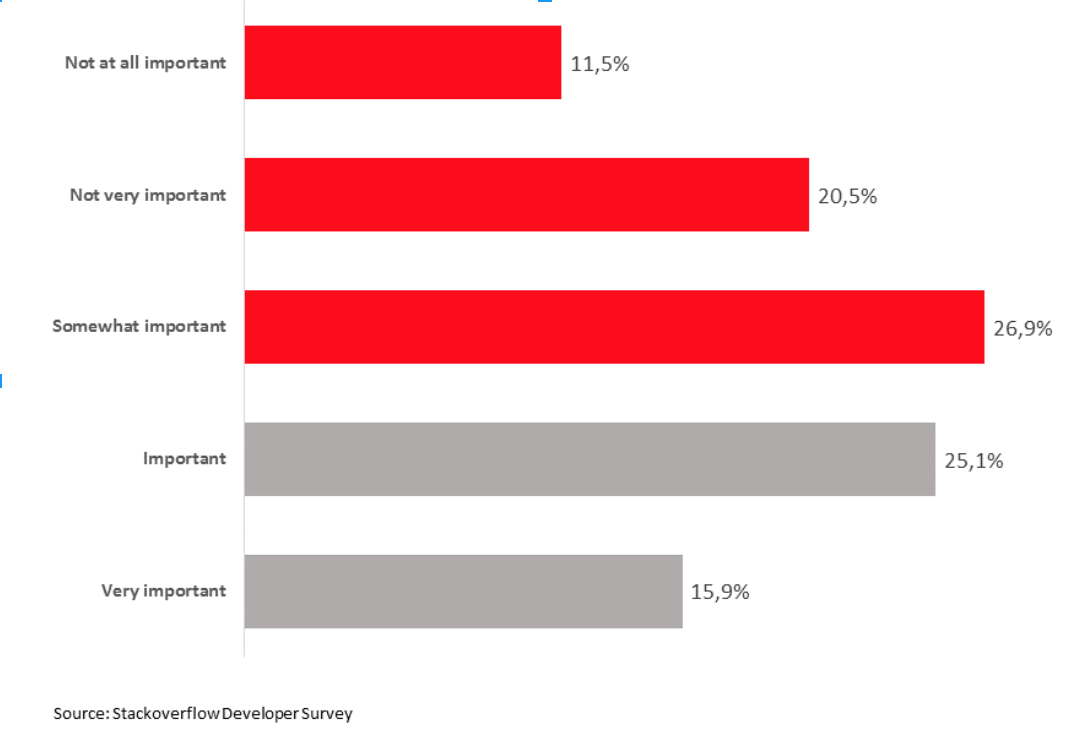
Figure 2: The importance of Formal Education among Developers


